Symptoms: joint pain.
Possible causes: trauma, arthritis, joint disease, osteoarthritis.
Doctor: The therapist records the complaint, sends it for examination, and then refers the patient to a doctor with a narrower professional scope based on the examination result.
Treatment: prescribed separately in each case.
Prevention: Reduce the load on joints, maintain a healthy lifestyle, seek medical attention and eat in time.
Why do joints hurt?
Joints can be injured for two reasons: arthritis, inflammation of the joint tissue, or arthropathy (osteoarthritis), which is a degenerative dystrophy process in which the osteochondral component of the joint is destroyed. The diagnosis should be made by a doctor, but you can resolve the symptoms yourself.
The inflammation in arthritis is like a forest fire: everything starts to violently, and the joints will swell and aches even when you are resting, and the pain will increase when you try to do the slightest exercise. The skin in this area will turn red and feel hot to the touch.
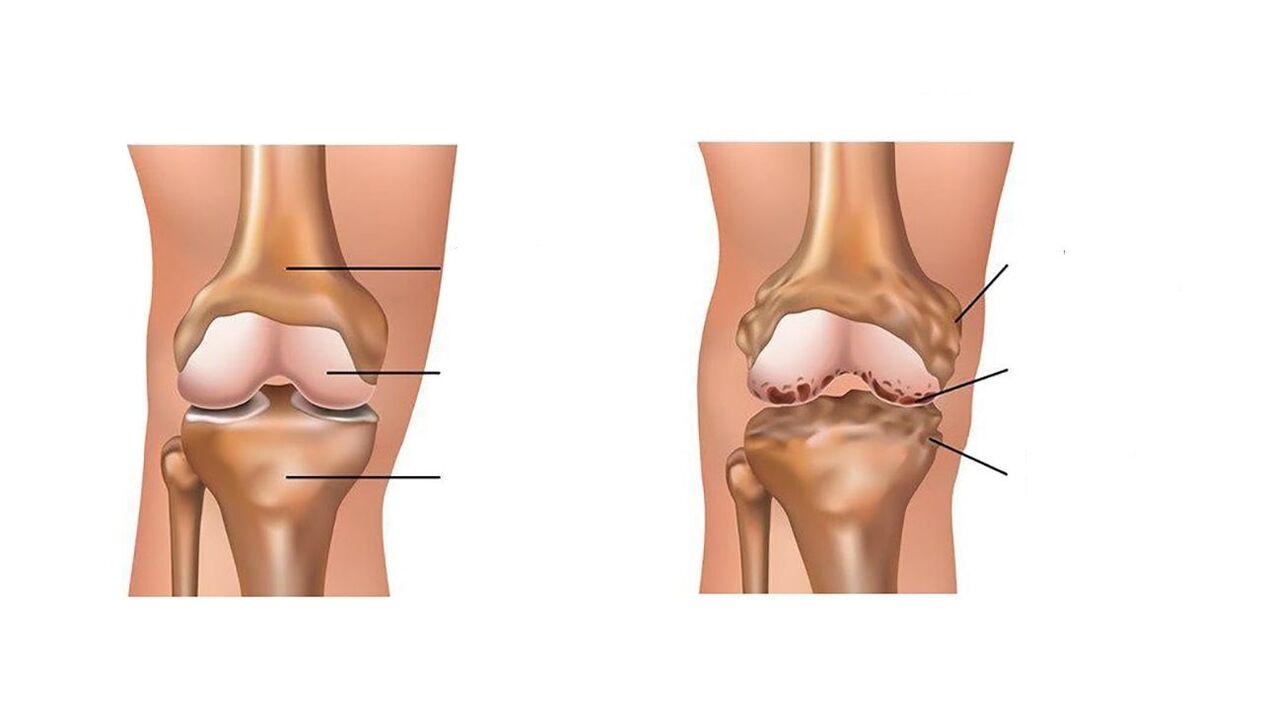
For arthropathy, everything is different: the joints are initially slowly destroyed unknowingly. Joint pain, which is mild and painful at first, only appears during exercise, and is quite tolerable. It increases over time and becomes continuous and severe enough to disrupt calm and sleep. The insidious part of this pain is that it is related to pathological processes that occur in the joints and only occurs when X-ray images show signs of damage to the corresponding joints. Unfortunately, this is irreversible. This is a sign of the proliferation of spines (marginal osteophytes) along the edges of the articular surface of the bones that form the joints, narrowing of the joint space, and signs of bone sclerosis-areas of pathological increase in bone density. If arthropathy affects one joint, such as the knee joint, the biomechanics will change and the function of the adjacent joints (hip and ankle joints) will be disturbed. Their load increases, and the load is uneven, so they wear faster. As a result, arthropathy affects one joint, the pain increases and may spread to all new joints.
Type of pain
The type and nature of pain sensations depend on the cause of them.
In the context of high temperatures (up to 40°C), joints can be painful due to flu and acute respiratory infections. Once the temperature returns to normal, the pain will go away on its own without special treatment.
For arthritis pain:
- sharp,
- pain,
- pulsation
- shooting,
- Occurs at rest and exacerbates during certain exercises
- Given to neighboring areas,
- When probed (palpated), it will be injured everywhere on the entire surface of the joint, especially along the joint space.
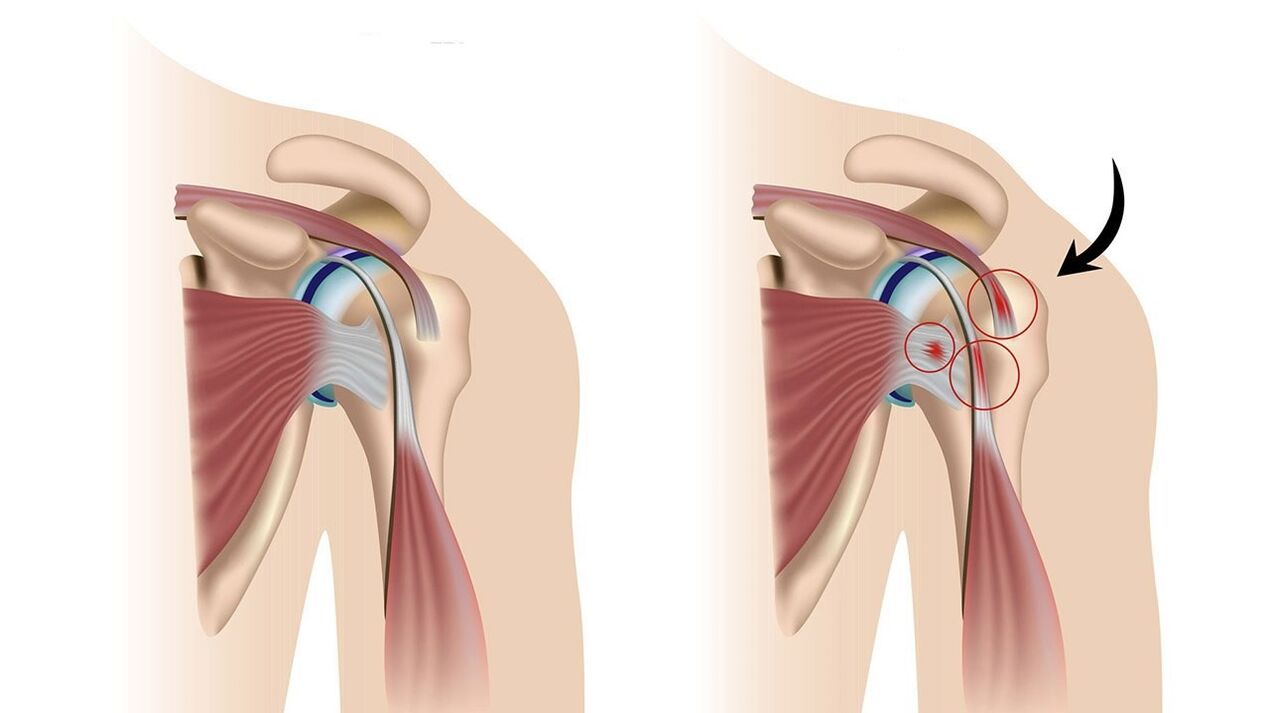
Periarthritis is particularly unbearable-inflammation of the tissues around the joints (its pockets, tendons, and ligaments). How everything happened can be explained by the example of the shoulder joint. First, the joints begin to ache. The pain quickly became unbearable, almost unbearable. It sends a signal to the shoulder blades and neck area, which is intensified (and often accompanied by tightening) when trying to stretch the arms to the sides of shoulder level or bend at the elbows and put them behind the back. At the end of the collarbone, it is located on the front shoulder joint, and there is a pain point in the same place at the back. When you press them with your fingers, the pain will increase. With such a keen sense, the joints need to be fixed-the hand needs to be hung on the handkerchief, try not to move it. This is a necessary condition for successful treatment.
important! Choose adequate analgesic and anti-inflammatory treatment as soon as possible after the examination. This will reduce the severity of joint inflammation, reduce pain and improve quality of life.
For arthropathy, joint pain is different:
- The pain is mild and inconsistent at first, and is characterized by wavy—in certain periods, it can last for weeks or even months. But over time, without treatment, the waves of pain will become stronger and more frequent, and the gap between them will shrink.
- Pain at the beginning: It exploded on the first attempt to take a step, raise the arm, and bend over. Then the joints seemed to develop and the pain eased.
- Mechanical rhythm-joints begin to ache when loaded. At first, high loads will cause pain-lifting weights, running stairs, walking for long periods of time, exercising. Later, even slight movements echoed the pain. But at the same time, unlike the unpleasant feeling of arthritis, when you rest and calm your joints, the pain of arthropathy will disappear. This is why doctors talk about mechanical rhythms: exercise causes pain, and rest reduces pain.
- Discomfort at night. There is no pain when resting, but it is uncomfortable to lie down. You always want to change your posture and find a position where you can forget the joints and spine, but it does not work. Joint pain, that's it! Shackles in the morning: I woke up, there was no pain, but it was like being tightly wrapped in iron chains or swaddling-the joints did not listen, but the feeling of stiffness gradually disappeared, and the range of motion of the joints was restored.
- Protective posture. When the joints are painful, you need to take what is called analgesia-an analgesic posture in which it becomes easier. This is most obvious in the case of the spine: it also consists of joints. When one of them is wedged, the nerve root enters the bone vise, and acute pain based on sciatica occurs. Anyone can diagnose a patient with sciatica after seeing this poor man being twisted. In fact, with this "deflection" supported by muscle spasms, the body tries to minimize pain.
Hip and knee osteoarthritis
The pain of a hip injury (most often on one side) is located in the upper thigh and radiates to the knee. He usually starts to get sick in the second half of the day, when he has already worked a lot. The pain aggravated when walking, and weakened and disappeared when resting.
The knee joint most often suffers from these two diseases at the same time. They straighten easily and start to hurt when bent. The so-called staircase symptom is a characteristic of knee joint disease. Downhill is more painful than climbing; the patient does this by turning sideways. Sometimes, due to osteophytes (osteophytes) or fragments thereof (for example, bone fragments "lost" in the joint are called "joint mice"), the joint will be wedged into a curved position. When trying to bend or straighten the joint, joint blockage will increase the pain.
Knee mobility problems are not always related to arthritis. Sometimes joint wedging can be "wrong". The most common causes of false knee joints include:
- Edema (excessive fluid in the joint capsule can interfere with adequate flexion and extension of the joint).
- Inflammation (inflammation of the knee tissue, such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout).
- Incorrect movement of the kneecap in the joint (with severe pain).
- Stimulates the tissue lining the joints.
- Knee injury (any serious knee injury, such as a sprain, will cause muscle cramps).
important! If the joint is stuck and the joint cannot be actively moved, it is necessary to seek medical help from an orthopedic trauma specialist—emergency room, clinic, and hospital as soon as possible. Don't hesitate to call an ambulance-this is a good reason to call, because you can't go very far with one leg, and you may not even be able to reach the clinic yourself.
diagnosis
Depending on the nature of the pain and the appearance of the affected joint, even non-experts can make a preliminary diagnosis (arthritis or arthropathy). But quickly go to the regional clinic to confirm the hypothesis!
Which doctor should I see?
If joint pain occurs, you should make an appointment with a local therapist. He performs the functions of a medical dispatcher: he records complaints and clinical symptoms, guides patients to conduct examinations, and based on the results of the examinations, decides to consult the doctor for each specific patient. Various experts are involved in maintaining joint health:
- Arthrologist.
- Orthopedic traumatologist.
- Rheumatologist.
- Chiropractors (if the spine joints are affected).
- Podiatrist (when it comes to foot joints).
- Surgeon.
- Oncologist.
- Neurologist (if the joint has been treated but the pain is still there).
- Nutritionist (if the joint is injured due to a metabolic disorder, such as gout, or is overweight).
Which tests are to be passed and what research is to be conducted?
The inspection starts with the simplest-clinical (from the fingers) and biochemical (from the vein) blood tests for signs of inflammation, and general urine tests. In some joint diseases, the kidney is involved in the pathological process. Excessive uric acid in the urine may indicate that gout is the cause of joint disease.
Laboratory studies of synovial fluid in the joints help to detect the inflammatory process and clarify its nature. It is obtained by puncturing the joint capsule-puncture. If necessary, perform histological examination of the synovial fragments lining the joint cavity from the inside.
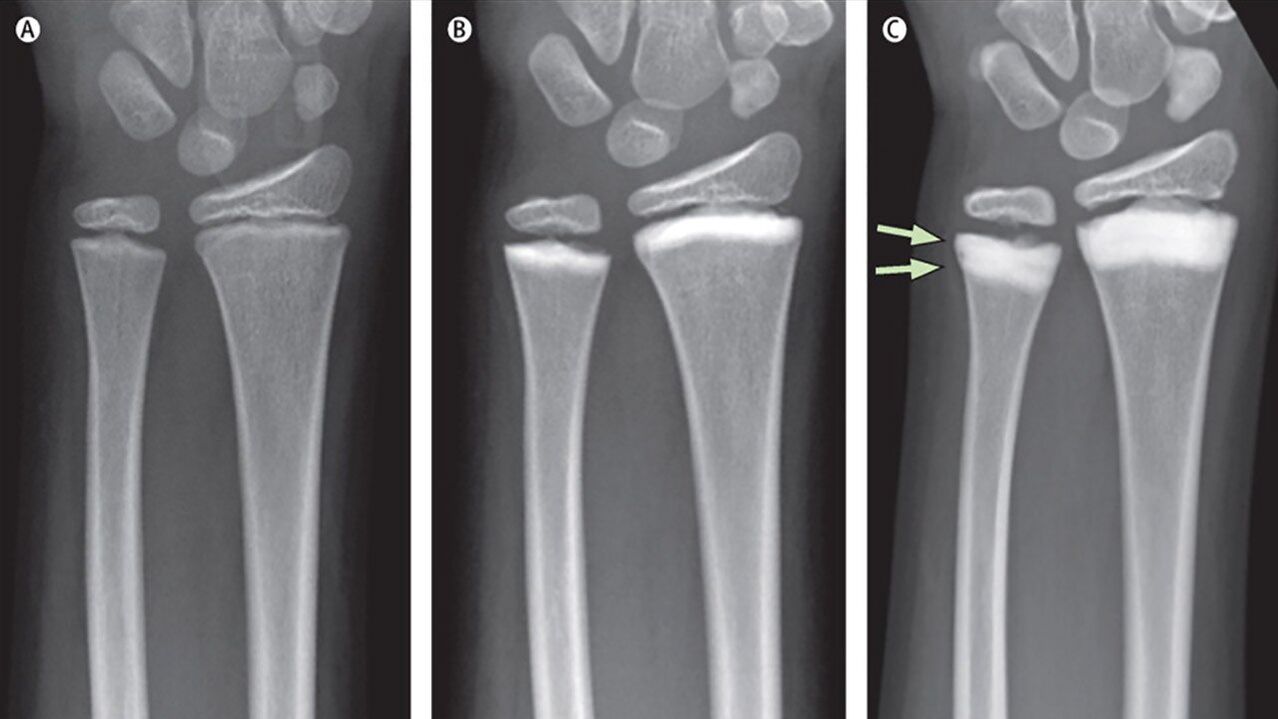
An effective diagnostic method is to perform X-ray examination of the joints in two standard projections. It will help visualize the narrowing of the joint space, bone hyperplasia, osteoporosis and bone sclerosis (areas of decreased and increased bone density.
Currently, comprehensive information on the state of joints is provided through magnetic resonance imaging.
Which joint diseases cause pain?
There are more than one hundred such diseases. In the elderly, arthropathy is common, while in young people, rheumatoid arthritis and injuries (bruts, fractures, ligament injuries) are common.
"Along with arterial hypertension, commonly referred to as hypertension, joint disease ranks among the most common reasons for seeking medical help. Patients experience chronic pain at the same time, so they are unable to live and work fully. This is not only a medical problem, but also aAn important social issue, said the doctor of medicine and the professor of the Department of Rheumatology. - Among all joint diseases, arthropathy is the most common. 97% of people over 65 suffer from this disease. If we talk about jointsThe chronic inflammatory disease-arthritis, then rheumatoid arthritis is prominent. It is not a gift, not only because of the pain syndrome: within 3-5 years after the onset, this type of arthritis inevitablyThe disability group was assigned to the patient and ended. "
How to get rid of joint pain urgently?
Analgesics can overcome pain quickly: if you don't want the pain to change from acute to chronic, you can't tolerate it anyway. This transformation can happen quickly-within 3-4 weeks, so getting rid of joint pain should be an urgent task. Once you put pressure on it, the joints will start to hurt. Therefore, when pain occurs, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with a good analgesic effect should be taken half an hour before any physical activity.
If the joint pain worsens at night, in addition, before going to bed, the doctor will recommend taking Analgin sodium and Drotaverine containing niacin to improve local blood circulation.
Local treatment
NSAIDs have a terrible side effect-they can damage the gastric mucosa until the formation of ulcers, so they tried to apply them topically as part of various ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. They are usually applied to the skin of the affected joint twice a day. Special plasters with magnetic powder applied to joints or spine can also relieve pain.
What if the joints are not treated?
If joint diseases are not treated in time, they can cause mobility and disability. If one or more large joints are affected, artificial joints can be used instead. Multiple joint injuries (polyarthritis) are usually the result of general diseases of the body (such as psoriasis). In this case, starting the disease is even more dangerous because it progresses rapidly and can cut your life quite quickly.
in conclusion
Almost everyone is familiar with joint pain, and there are two main reasons for its occurrence-inflammation (arthritis) or destruction of bones and cartilage (arthropathy). Interestingly, the joints on the arms and legs can be injured in different ways. In the upper limbs, as opposed to the lower limbs, it is usually not the joints themselves that are affected, but the surrounding tissues (tendons, ligaments, pockets). This is due to the different types of loads on the arms and legs-dynamic and static respectively. It is necessary to fight joint pain from day one: the prospect of disability in the next 10 to 15 years will satisfy very few people. As part of preventing joint diseases, it is very important to lose extra weight to reduce joint pressure and cope with accompanying diseases (allergies, diabetes).































