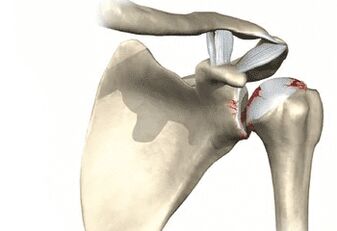
symptoms and causes
- Atherosclerosis and other chronic blood vessel-related diseases result in impaired blood circulation to the cartilage tissue in the shoulder.
- Autoimmune chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Endocrine system dysfunction (diabetes).
- Congenital shoulder joint anomalies, infant birth injuries, and other injuries that lead to pathological deformation and dysfunction of limbs.
- Acquired lesions of joint structures after injury or accident, failed surgery, including inflammation caused by arthritis, synovitis, osteoporosis, etc.
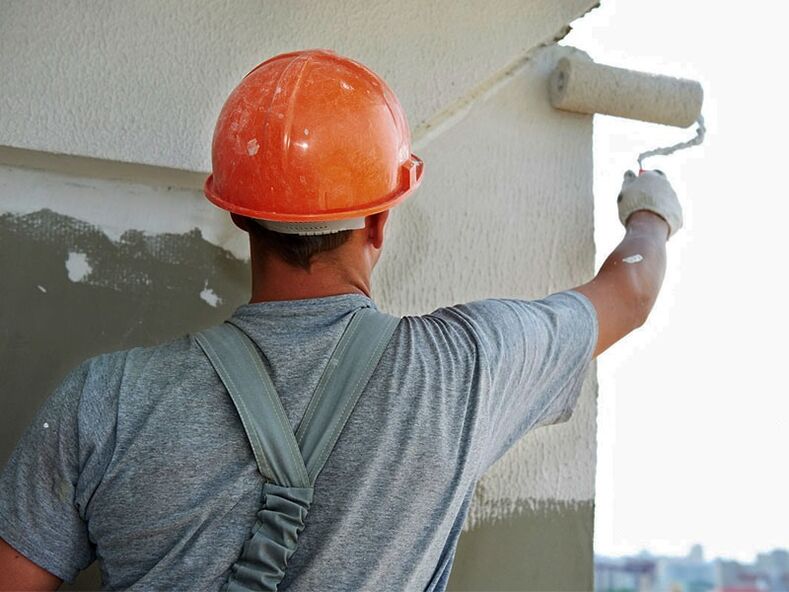

- Occupational activities in which the shoulder joint is subjected to heavy loads day after day for many years - shoulder arthrosis is rightly called a disease of plasterers, painters and loaders;
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity - lack of exercise, slowed blood circulation, joint tissues do not get the nutrients they need and begin to atrophy;
- Overweight – often in combination with pre-existing factors; obesity can prevent a person from being active and joints can be put under additional stress from increased weight;
- genetic predisposition;
- Older adults – About 80% of people over the age of 70 show symptoms of osteoarthritis.
How to recognize disease
- Visible joint swelling and deformation;
- The joint skin becomes red and the local temperature increases;
- The characteristic crunching sound in the joints. The squeaking sound that occurs when the hand is moved violently is caused by cracks in the cartilage and the accumulation of salt between the joint elements. At first, the crunching only occurred with sudden movements; it was quiet and almost inaudible. In advanced forms of the disease, the shoulders creak with every movement, a sound that can be heard by others;
- Limb movement is limited. When examining a patient, the doctor will ask him to comb his hair. This test is enough to diagnose shoulder osteoarthritis: The patient will feel severe pain, make rotational movements of the shoulder, have difficulty moving the shoulder backward, and the doctor will hear cracking and clicking sounds in the joint.
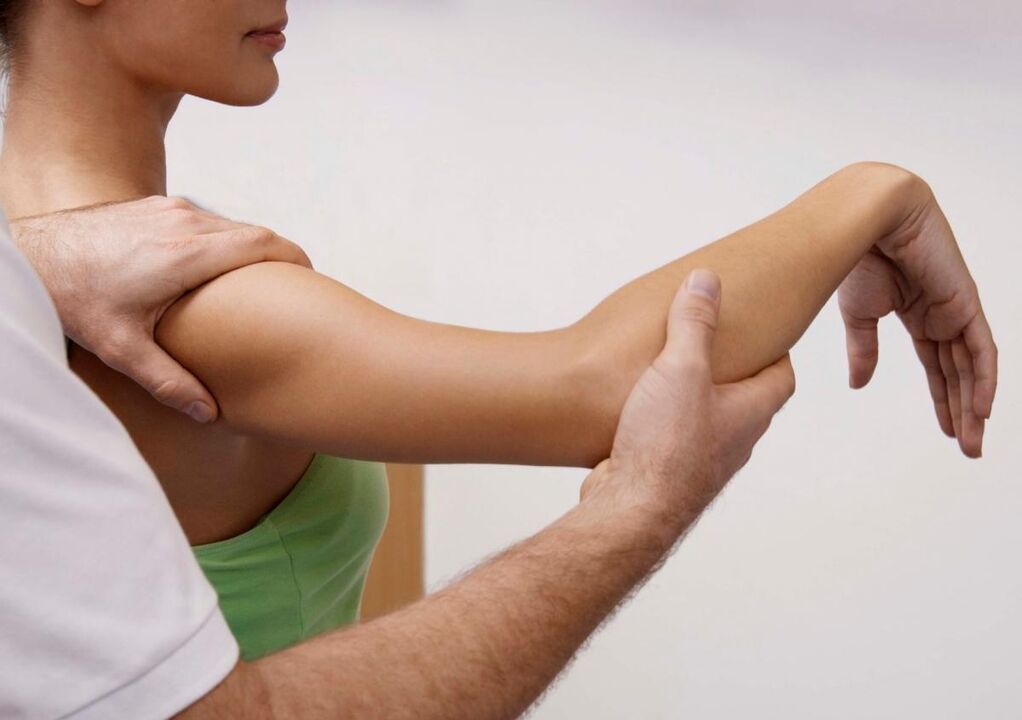
degree
- Level one.At this stage, the disease is just beginning to develop and changes in the cartilage tissue are still minimal. The main symptoms of grade 1 DOA are joint and limb weakness and periodic, persistent pain. Pain occurs after physical exertion and during prolonged, monotonous, repetitive hand movements. After a night's sleep or a long period of rest, a person will feel stiffness in the shoulder joint, but as the condition progresses, this stiffness will still disappear without medication and physical therapy - a slight warm-up is enough. If X-rays are taken at this stage, the images will not show significant changes in the joint structure, but cartilage thinning and deformation may be evident.
- second degree.Pathological processes proceed and manifest themselves more actively. A person is accustomed to the fact that his shoulders hurt after get off work, he "waits" for the pain, prepares painkillers and ointments for joint pain, from the pharmacy or homemade. Diagnostic X-rays will show noticeable changes in the joint: thinning and deformation of the cartilage, inflammation of the joint membrane. The joints may become red and swollen from time to time; they may make crunching, creaking, and clicking sounds when moved.
- Level three.The shoulder joint is constantly aching and creaking, and in order to relieve discomfort, the patient tries not to touch it or move the limb. The deformity is visually apparent; the affected shoulder differs in size and shape from a healthy one; it often becomes red and swollen, accompanied by increased pain. They cannot be removed with painkillers.
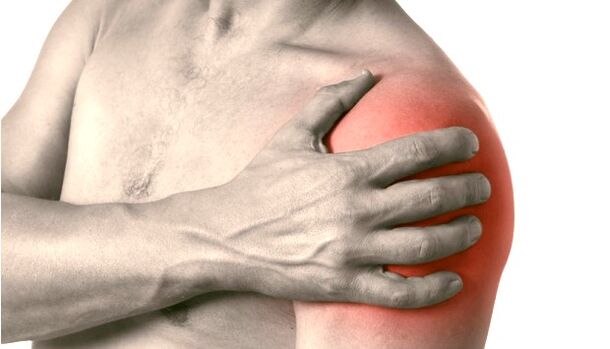
Remark:In medical practice, it is extremely rare to encounter grade 3 shoulder arthropathy. Typically, patients seek medical help and begin treatment as early as possible. If for some reason the patient cannot see a doctor, or if the patient lives in unfavorable social conditions and there is no qualified doctor, severe destruction of cartilage can occur against the background of extensive trauma.
How are joint diseases diagnosed and treated?
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- In some cases, ultrasound can provide a complete picture of the condition of a joint;
- Clinical urine and blood tests - white blood cell count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate will be assessed. If they are too high, inflammatory processes can occur in the body.
- A course of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug is prescribed in the form of oral tablets or powder or external ointment to eliminate the main symptoms of inflammation - pain, swelling, redness, increased body temperature.
- An anesthetic used to treat severe pain, in the form of tablets or injections. These drugs cannot be taken continuously; they do not eliminate the cause and are only used in extreme cases where the pain is unbearable.
- A course of chondroprotectants - medications that promote the recovery of cartilage tissue and prevent further destruction. They can also provide partial relief from pain, swelling, and deformity of the shoulder joint. These medications do not work immediately and need to be taken for at least 3-4 months.
- Muscle relaxant treatments - tablets or injections to relieve muscle spasms. These are optional medications in the complex treatment of osteoarthritis; they are not always prescribed.
- A course of vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements containing collagen and hyaluronic acid.
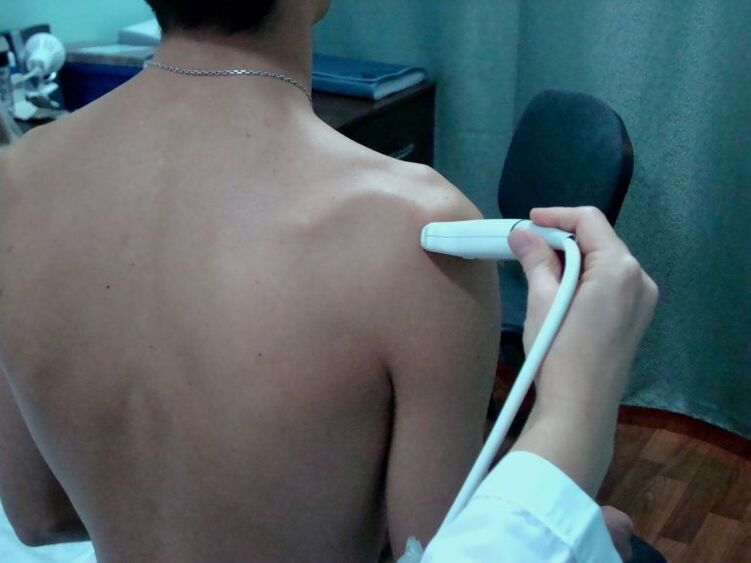
- cryotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis;
- Laser Treatment;
- magnet therapy;
- mud therapy;
- Various types of massage;
- physiotherapy.
Helpful advice:Shoulder pathologies of grade 1-2 can be treated at home with the additional use of folk remedies. Most importantly, patients do not forget to take their medications on time, nor do they skip physical procedures - only by regularly and conscientiously following all the doctor's prescriptions will the results be noticeable and long-lasting.
































